Introduction
In the context of our technology-driven lives, it’s essential to grasp the facts about computer viruses. Imagine a computer virus as a tiny, bad program, very different from the good software, like games or useful apps that makes our computer work better. Instead, these are stealthy fragments of code with the capacity to afflict your computer with ailments or work in way around for which they are not mend to do.
Table of Contents
History of Computer Viruses
A. Tracing the Origins of Digital Malice
Let’s go back in time to when computers were just starting to grow. Some clever folks, instead of using their skills for good, started creating tricky computer programs. These programs were like digital pranks, meant to mess with other people’s computers. That’s how computer viruses were born.
B. Landmark Moments in the Evolution of Computer Viruses
As time passed, these computer viruses got smarter and sneakier. They learned new tricks to hide and spread in within the networks. One significant moment in their history was when they started using the internet to travel from one computer to another. This made them even more challenging to stop.
C. A Dive into Notable Viruses in History
Some computer viruses became infamous just like famous villains in stories. They caused big problems for lots of people. One of these was the “ILOVEYOU” virus, which spread through emails, causing chaos. Another was “WannaCry,” which took over computers and demanded money from their owners. These viruses are like cautionary tales, showing us how much damage computer viruses can do.
Remember, the history of computer viruses is a bit like the history of troublemakers in the digital world. They started small, but as technology grew, so did their mischief.
How Computer Viruses Work or Attack other Computer.
A. The Intricate Web of Infection

Imagine a computer virus as a sneaky bug that gets into your computer when you open an email or a file from an unknown source. It’s like when you catch a cold from being around someone who’s sick. Computer viruses use tricks to slip past your computer’s defenses, just like a crafty burglar might find a way into a locked house.
B. Replication Tactics: How Viruses Multiply
Once inside your computer, a virus is like a copy machine that makes more and more of itself. It’s similar to a plant that grows from a single seed into many plants. These new virus copies then go on to infect other parts of your computer, just like a rumor can spread from person to person.
C. Cloaked in Deception: Concealment Techniques
Computer viruses hide in your computer, making it hard to find and remove them. It’s like a cleverly hidden treasure that’s challenging to discover. They can use tricky disguises, like pretending to be regular computer files or mimicking the names of important programs you use every day. This camouflage makes them tough to spot.
D. The Venomous Payload: How Viruses Attack Computers
When the virus decides it’s time to cause trouble, it’s like a hidden trap that suddenly springs to life. For example, it might start deleting your important files, just like a prankster might mess up your room when you least expect it. Some viruses can even spy on what you do on your computer, like someone secretly watching your every move. They can be very harmful, just like a poisonous snake’s bite.
Different Types of Computer Viruses:
Exploring the Diverse World of Digital Infections
Just as there are many different kinds of tricksters and pranksters that can cause people trouble, there are various types of computer viruses that can harm your computer in different ways. These computer viruses have their own unique characteristics and sly tricks.
Think of your computer like a bank, and computer viruses as burglars trying to break in. These burglars have various tactics. Some sneak in and hide inside the bank for days, waiting for the right moment to steal. Others use tricks to convince the bank staff to open the doors for them. For instance, the “ILOVEYOU” virus, which spread through emails, was like a sneaky trickster convincing people to open a love letter. Some viruses can even lock up your files and demand a ransom, just like a kidnapper might ask for money to release a hostage. The “WannaCry” virus did just that, causing a lot of trouble over 150 countries, infecting hundreds of thousands of computers worldwide.
In this section, we’ll take a closer look at these different types of computer viruses, including examples from the past, and learn what makes them unique. Understanding them is a bit like studying the different illnesses that affect people – knowing what they are helps you protect yourself and your computer better.
Different Types of Computer Viruses:
Exploring the Diverse World of Digital Infections
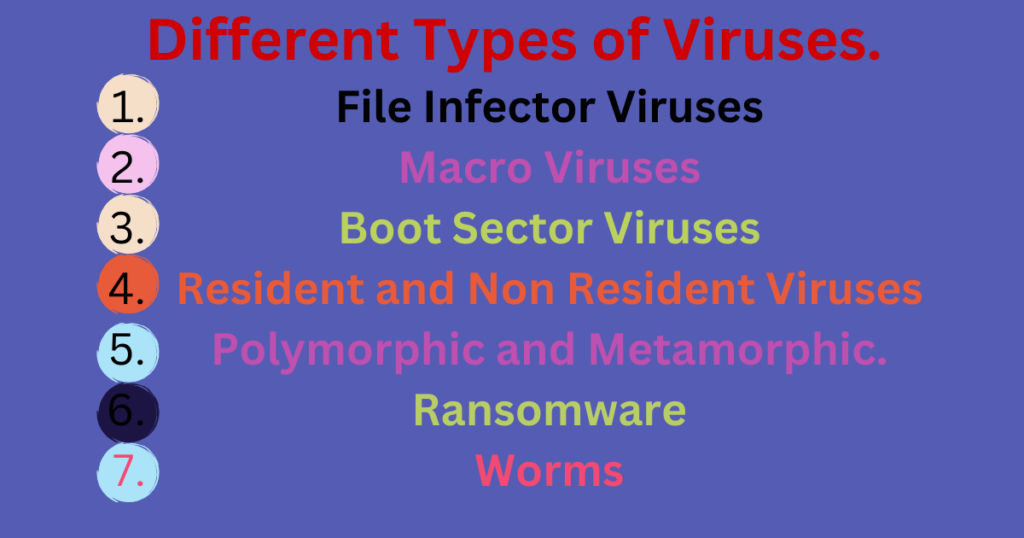
- File Infector Viruses: File infector viruses attach themselves to executable files (programs) and modify them so that they can spread to other programs when the infected program is run. They can corrupt or alter the functioning of affected programs.
- Macro Viruses: Macro viruses infect the macros in documents like Word or Excel files. When you open an infected document, the macro virus can execute malicious actions, such as spreading itself to other documents or corrupting data.
- Boot Sector Viruses: Boot sector viruses target the master boot record (MBR) of a computer’s hard drive or removable storage devices. They can prevent the computer from starting up properly and may lead to data loss.
- Resident and Non-Resident Viruses: Resident viruses embed themselves in a computer’s memory and can operate without the need for a host file. Non-resident viruses depend on a host file to spread and execute.
- Polymorphic and Metamorphic Viruses: Polymorphic viruses can change their code each time they infect a new host, making it difficult for antivirus software to detect them. Metamorphic viruses go a step further by completely rewriting their code with each infection.
- Ransom ware: Ransom ware is a type of malware that encrypts the victim’s files, rendering them inaccessible. The attacker then demands a ransom, usually in crypto currency, in exchange for the decryption key.
- Worms: Worms are standalone malicious programs that can replicate themselves and spread across computer networks without needing a host file. They often exploit vulnerabilities to infect other devices.
More facts about computer viruses and how it spreads

Imagine your computer as a fortress, and computer viruses as crafty infiltrators trying to breach through its defenses. These clever digital infiltrators find multiple ways to sneak into your digital fortress, much like resourceful individuals who devise methods to breach a building’s security.
Following are the ways or means by which computers can get infected with Viruses.
1. Infected Files and Downloads:
Consider infected files or downloads as concealed traps. Imagine you receive an email attachment that appears harmless, perhaps a document labeled ‘Important Business Proposal.’ But you don’t know that it’s hiding a virus. When you open it, the virus silently infiltrates your computer, just like a master of disguise slipping into a crowd. An illustration of this is the ‘Melissa’ virus, which spread through seemingly innocent email attachments, just like “Anna Kournikova” virus did the same way in 2001.
2. Malicious Websites:
Think of bad websites as traps set by online crooks. Sometimes, you might end up on a site that seems okay, like going into a building that looks fine from the outside. But hidden inside, there are dangers. Your computer can catch a virus just by going to such a website. For example, ‘Phishing’ sites pretend to be real ones and trick people into sharing important information like passwords or credit card numbers. Common examples include fake banking websites that ask for your login details or counterfeit shopping sites that aim to steal your payment information.
3. Removable Media (USB Drives, External Hard Drives):
Think of removable media, such as USB drives or external hard drives, as modern-day Trojan horses. At first glance, they appear harmless, like friendly messengers bearing gifts. However, beneath their innocent exterior, they might harbor concealed threats, much like the legendary wooden horse of Troy, which hid Greek soldiers.
When you connect one of these devices to your computer, it’s like unlocking the door to your digital treasure. You’re essentially allowing whatever is on that device to enter your computer, similar to how the Trojans unknowingly allowed unexpected Greek visitors.
For instance, consider a scenario where a friend lends you a USB drive, seemingly filled with vacation photos. You innocently connect it to your computer, thinking you’re about to relive some happy memories. Innocently you might attach a USB that carries a malware payload that will infect your computer upon connection. In this way, it’s a bit like the famous ‘BadUSB’ attack, where a seemingly harmless USB device turns into a malicious weapon once plugged in, compromising your computer’s security.
4. Software Vulnerabilities:
Think of software vulnerabilities as weak spots in your fortress’s walls. These vulnerabilities are like open windows in your digital home, and sometimes, viruses take advantage of these weak points in your computer’s software to sneak in. Just like a burglar finding an open window in a house, viruses can exploit these vulnerabilities. By exploiting vulnerability in Adobe Flash Player in 2020, cybercriminals were able to launch attacks on computers, potentially compromising sensitive data.
For instance, the ‘WannaCry’ ransomware attack in 2017 targeted a specific vulnerability in Microsoft Windows that many users hadn’t patched with the necessary security update. By exploiting this weakness, the ransomware gained access to countless computers worldwide, encrypting files and demanding a ransom for their release. This incident served as a stark reminder of the importance of regularly updating and securing your computer to protect against such attacks.
Symptoms of a Virus in the Computer: Recognizing the Tell-tale Signs of Infection
In this section, we delve into the warning signals that your computer might be infected. Common symptoms include a noticeable slowdown in performance, unexpected crashes, and strange pop-up messages. Recognizing these signs early is vital in taking swift action to protect your system and data.
How to Secure Your Computer from Viruses:
A. Fortifying Your Digital Fortress with Antivirus Software
Antivirus software acts as a guardian for your computer, constantly monitoring for potential threats. We’ll explore the importance of selecting reliable antivirus programs and how they can safeguard your system from malicious software.
B. Vigilance through Updates and Patches
Keeping your operating system and software up to date is akin to locking the doors and windows of your digital home. We’ll emphasize the critical role of regular updates and patches in closing vulnerabilities that cybercriminals often exploit.
C. Navigating the Web Safely: Best Practices
The internet is a vast and sometimes untrustworthy territory. Here, we’ll provide essential tips for safe web browsing, including avoiding suspicious websites, being cautious with downloads, and practicing secure online behaviors.
D. Beware of the Inbox: Email Security
Email remains a primary vector for malware distribution. We’ll discuss strategies for identifying and handling suspicious emails, ensuring your inbox doesn’t become a gateway for digital threats.
E. A Safety Net: Data Backup Strategies
Backing up your data is like having an insurance policy against data loss due to virus attacks or hardware failures. We’ll explore various data backup methods, from external drives to cloud storage, to ensure your important files are protected.
How to Remove a Virus from the Computer: Steps to Safely Eliminate Digital Threats
If your computer does become infected, it’s crucial to act swiftly. We’ll outline steps to safely and effectively remove viruses, including running antivirus scans, quarantining infected files, and seeking professional assistance if needed.
Famous Virus Incidents:
A. The Love Letter that Wreaked Havoc: ILOVEYOU Virus
This section explores the havoc caused by the infamous ILOVEYOU virus, which spread through email attachments, disrupting countless computer systems and highlighting the need for robust email security.
B. Mydoom: A Modern Menace
Mydoom was a destructive email worm that rapidly spread in the early 2000s. We’ll delve into its impact on email systems and lessons learned from this modern menace.
C. Conficker: The Worm That Wouldn’t Die
Conficker was a persistent and adaptable worm that posed a significant threat. We’ll examine its ability to evade detection and the challenges in eradicating it.
D. WannaCry: A Global Cyber Crisis
WannaCry was a ransomware attack that made headlines worldwide. We’ll discuss its rapid spread and the global cyber crisis it created, underscoring the importance of timely software updates.
E. Stuxnet: The Cyber Weapon of Mass Destruction
Stuxnet was a highly sophisticated cyber weapon designed to disrupt Iran’s nuclear program. We’ll explore the unique characteristics of this digital weapon of mass destruction and its implications for cyber warfare.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding computer viruses is paramount in the digital age. We’ve explored the symptoms of an infected computer, ways to secure your system through antivirus software, updates, safe web practices, email security, and data backups. We’ve also discussed the essential steps to remove viruses safely. Additionally, we’ve taken a historical journey through famous virus incidents, highlighting the real-world consequences of these digital threats.
It’s clear that vigilance is the key to maintaining a secure digital environment. Cybercriminals’ tactics evolve in tandem with the advancement of technology. Staying informed and implementing best practices for computer security are essential in safeguarding your digital world. In this ever-changing landscape, the imperative of vigilance cannot be overstated.
