Introduction:
What draws you here is the question, ‘What is a content marketing?’ or ‘Which of the following provides an accurate definition of what a content marketing campaign involves?’
Table of Contents
Content marketing campaigns are strategic efforts by businesses to create and share valuable content, like blog posts, videos, and social media updates, to engage their target audience. The main goal is to build trust and credibility, addressing the audience’s specific needs, while subtly showcasing the brand’s expertise. This involves careful distribution and analytics to measure effectiveness. In essence, it’s about delivering value to the audience.
Definition of Content Marketing.
Content marketing, as defined, is the strategic practice of developing and promoting online materials with the aim of increasing interest in a product or service. This multifaceted discipline involves creating a variety of digital content, including articles, videos, info graphics, and social media posts, all tailored to engage a specific target audience.
Let’s start learning more about Content Marketing, step by step.
Chapter 1: What Is a Content Marketing?
According to Joe Pulizzi, a prominent figure in the field of marketing, defines content marketing as: “A strategic marketing approach focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience — and, ultimately, to drive profitable customer action.”
Explanation: Joe Pulizzi emphasizes the deliberate nature of content marketing, where businesses create and share content that holds value for a specific audience. The goal is to not only capture their attention but also to keep them engaged over time, ultimately driving actions that benefit the business.
As other famous author Seth Godin puts it,“Content marketing is the only marketing left.”
Explanation: Seth Godin’s statement underscores the paramount importance of content marketing in contemporary marketing practices. It suggests that traditional advertising methods have diminished in relevance, with content marketing now occupying the central role in connecting with and engaging audiences. In essence, it signifies that creating and effectively sharing valuable content has become the cornerstone of successful marketing in the digital age.
Chapter 2: Fields where Content Marketing is used.
Content marketing is a versatile strategy used across various fields and channels to engage, inform, and convert audiences. Here’s how it’s applied in different areas:

- Email Marketing:
Content marketing is used in email campaigns to provide valuable content such as newsletters, product updates, or educational materials to subscribers. Building trust and keeping the audience engaged is main motivate to use content marketing.
- Social Media Marketing:
On platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn, content marketing involves creating and sharing content like blog posts, videos, info graphics, and more to attract, entertain, and inform followers.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization):
Content marketing plays a crucial role in SEO by producing high-quality, relevant content that ranks well in search engine results pages. Blogs, articles, and website content are optimized with keywords to attract organic traffic.
- PR (Public Relations):
Content marketing can be used in PR strategies to create press releases, thought leadership articles, or guest posts that enhance a brand’s reputation and authority in its industry.
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click) Advertising:
Even in paid advertising campaigns, content marketing is essential. Ad copy and landing page content need to be compelling and relevant to attract clicks and conversions.
- Inbound Marketing:
Content marketing is the backbone of inbound marketing. It involves creating valuable content that draws potential customers in, nurtures them through the buyer’s journey, and ultimately converts them into customers.
- Digital Marketing:
Content marketing is a fundamental component of digital marketing as a whole. It encompasses various online channels and strategies to promote products or services using digital content.
- Content Marketing (Itself):
Content marketing is often used to promote content marketing services or products. Agencies and consultants may create educational content about the value of content marketing or share case studies showcasing their success.
Chapter 3: What is a Content Marketing, Its Purpose or goal?
Brand Loyalty: Content marketing aims to build and strengthen brand loyalty by consistently providing valuable and relevant content that resonates with the audience, fostering trust and long-term relationships.
Customer Education: Content marketing seeks to educate customers by addressing their queries, concerns, and needs. It provides informative content that empowers customers to make well informed decisions and get the most value from products or services they are planning to opt for.
Brand Awareness: Content marketing plays an important and crucial role in increasing brand awareness. By creating and distributing content that is shareable and resonates with the target audience, it expands the reach and visibility of the brand to each and corner that possible.
Talent Recruitment: Content marketing can be used to attract top talent by showcasing the company culture, values, and opportunities. Sharing employee stories and insights can help in recruiting the right people.
Removing Roadblocks: Content marketing can address common obstacles or objections that potential customers might face during the buyer’s journey. By providing solutions and guidance, it removes roadblocks and facilitates the decision-making process.
Customer Engagement: Content marketing aims to engage customers on an ongoing basis. Whether through blog posts, social media, or interactive content, it encourages customers to interact with the brand and stay connected.
Traffic: Content marketing is instrumental in driving website traffic. High-quality, SEO-optimized content attracts organic traffic from search engines, while shareable content can bring in traffic from social media and other sources.
Lead Generation: Content marketing generates leads by capturing the interest of potential customers. It often includes lead magnets such as eBooks, webinars, or email subscriptions to collect contact information for further engagement.
Chapter 4: The Positives of Content Marketing or Benefits one can achieve using Content Marketing.
Informative and Educational:
Imagine you own a gardening supply store. Through content marketing, you regularly create blog posts and videos that teach your audience how to make garden took beautiful. Your articles provide step-by-step guides on topics like soil preparation, plant selection, and pest control. Your videos showcase practical demonstrations of planting techniques and garden maintenance.
Your audience, aspiring gardeners, relies on your content to gain knowledge and confidence in their gardening endeavors. Just like having a personal gardening expert at their disposal, your brand becomes a trusted source of information in the gardening community.
Builds Trust and Credibility:
Picture yourself as the owner of a small tech startup. You consistently produce blog posts and webinars that explain complex tech concepts in simple terms, helping your audience understand the latest innovations. You share insights, case studies, and troubleshooting tips.
Over time, your audience begins to trust your brand as a reliable authority in the tech industry. They have confidence that when they encounter a tech challenge, your content will provide the answers they need. It’s like being that knowledgeable friend in the tech world they can always turn to for advice.
Engages and Connects:
Consider you manage a local bakery. Through content marketing, you regularly post enticing images of your freshly baked goods on social media platforms. You also share stories about the history of your bakery, the people behind the scenes, and the secret family recipes passed down for generations.
Your audience not only craves your delicious treats but also feels a sense of connection to your brand. They comment on your posts, share their own baking experiences, and even organize meet-ups with fellow customers.
Your content has transformed your bakery into more than just a place to buy pastries; it’s now a vibrant community hub where people gather to share their love for baking.
Improves SEO:
Imagine you run an online bookstore. You consistently create detailed book reviews, author interviews, and literary analysis articles on your website. Your content aligns with what book enthusiasts are searching for online.
When someone looks for information about a specific book or author, your website’s content pops up in search results. Much like road signs that direct travelers to their intended destinations, your content serves as a guiding beacon, leading readers to explore your online bookstore.
As your website’s visibility improves in search engine rankings, more book lovers find their way to your virtual shelves.
Cost-Effective: Suppose you manage a startup fashion brand with a limited marketing budget. Instead of expensive TV ads, you focus on content marketing. You regularly produce fashion tips, style guides, and behind-the-scenes videos showcasing your clothing line.
Over time, your content gains a loyal following, and your audience eagerly anticipates your latest creations. The initial investment in content creation continues to pay off as your brand grows. Your content, like a smart financial decision, offers long-term value and a substantial return on your marketing investment, proving that content marketing can be a cost-effective strategy for businesses, especially those with budget constraints.
Chapter 5: The Challenges of Content Marketing
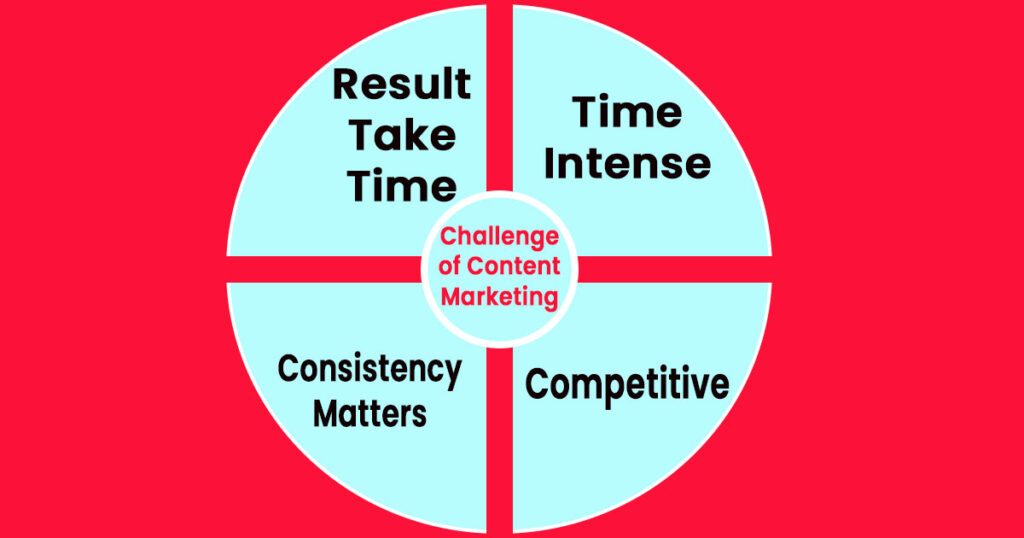
Time-Intensive:
Creating quality content is akin to crafting a fine piece of art. Just as artists invest time and effort into perfecting their masterpieces, content creators pour their expertise and creativity into each piece. It involves meticulous research, planning, writing, editing, and sometimes visual design.
Rushing the process can compromise the quality. So, while content marketing offers valuable returns, it’s essential to remember that it’s not a quick fix; it’s an investment that requires patience and dedication.
Competitive:
In the digital realm, the content landscape is like a bustling marketplace. There are thousands of businesses and individuals competing for attention, all offering their unique insights and solutions. Standing out in this crowded space is akin to differentiating your product in a saturated market.
It requires not only high-quality content but also creativity in presentation and promotion. To thrive, you must continually strive for uniqueness and find your niche within the vast content ecosystem.
Consistency Matters:
Consistency in content creation is comparable to maintaining a regular exercise routine. Just as regular workouts yield better results, consistently producing valuable content is essential for content marketing success. It’s about building a relationship with your audience over time.
When you consistently deliver value, your audience knows they can rely on you, and this trust is the bedrock of long-lasting connections and customer loyalty.
Results Take Time:
Content marketing is not as simple as flipping a switch to start a fan. It’s a complex process that requires time and effort, much like tending to a tree and waiting patiently for the fruits to bear after planting it. It’s a long-term strategy that requires nurturing and patience.
While some forms of advertising may provide immediate results, content marketing focuses on cultivating an audience and nurturing it over time. It’s about sowing the seeds of trust, credibility, and engagement. The harvest comes later, in the form of increased brand visibility, customer loyalty, and sustained growth.
It’s an investment in the future, and like all investments, it takes time to yield significant returns.
Chapter 6: Types of Content Marketing

Blog Posts:
Blog posts, a famous and widely used medium, enable businesses to provide valuable information to their viewers. They serve as informative articles that showcase a business’s knowledge and expertise on various topics related to their industry. These posts offer valuable insights to their audience and are typically published on the company’s website.
Videos:
Videos, a popular and highly engaging medium, allow businesses to convey information to their audience effectively. They are dynamic pieces of visual content that cover a wide range of topics. Videos are used to visually communicate information, often in a narrative or educational format. They are commonly shared on platforms like YouTube and various social media channels.
Info graphics:
Info graphics, a visually captivating format, serve as an excellent means for businesses to simplify complex concepts or data for their audience. They combine text, images, and graphics to present information in an easy-to-understand and engaging manner. Infographics are particularly useful for conveying statistics, trends, or step-by-step guides.
EBooks and Whitepapers:
EBooks and whitepapers are comprehensive resources that allow businesses to dive deep into specific subjects. These in-depth guides and reports offer valuable insights and solutions to their audience. EBooks and whitepapers are typically used as lead magnets to capture contact information from potential customers.
Podcasts:
Podcasts, an increasingly popular audio format, provide businesses with a versatile platform to reach their audience. They are audio content that can be streamed or downloaded and are accessible on various devices. Podcasts feature discussions, interviews, or presentations on a wide range of topics, making them a convenient way for audiences to consume content on the go.
Social Media Posts:
Social media posts, a quick and interactive medium, enable businesses to engage with their audience directly. These brief updates are shared on popular platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Social media posts play a crucial role in building brand awareness, fostering community engagement, and keeping followers informed and engaged.
Email Marketing:
Email marketing, a targeted communication method, empowers businesses to reach their audience through personalized messages. These emails contain valuable content, promotions, or updates and are instrumental in building and nurturing relationships with subscribers and customers.
Webinars and Live Streams:
Webinars and live streams, interactive real-time events, provide businesses with dynamic ways to engage and educate their audience. They typically include live presentations, Q&A sessions, and discussions. Webinars and live streams are valuable tools for connecting with an audience and sharing knowledge effectively.
Chapter 7: Creating Content Strategies.
Several key steps are involved in creating a content marketing. Here’s a outline of a content marketing strategy:
- Define Your Goals: Determine your specific objectives, whether it’s brand awareness, lead generation, customer retention, or something else.
- Know Your Audience: One must understand target audience’s demographics, interests, pain points, and preferences in order to achieve desire result out of content Marketing.
- Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords to optimize your content for search engines (SEO).
- Content Calendar: Develop a content calendar outlining what content to create and when to publish it.
- Content Creation: Produce high-quality, valuable, and engaging content, such as blog posts, videos, info graphics, or podcasts.
- Distribution Plan: Decide where and how to share your content, including social media, email, and other marketing channels.
- Promotion: Actively promote your content to maximize its reach and engagement.
- Measure and Analyze: Use analytics tools to track the performance of your content and adjust your strategy accordingly.
- Iterate and Improve: Continuously refine your content marketing strategy based on data and feedback.
- Content Amplification: Consider paid promotion or influencer partnerships to boost content reach.
- Engage with Audience: Respond to comments, messages, and feedback to foster engagement and build relationships.
- Document Your Strategy: Create a documented strategy that outlines your goals, target audience, content plan, and KPIs.
Chapter 8: Tools one might need for Content Marketing.
- For Content Creation and Editing:
- Grammarly: For grammar and spelling checks.
- Hemingway Editor: To improve readability and clarity.
- Canva: For creating visual content like info graphics and social media graphics.
- Adobe Creative Suite: For professional graphic and video editing.
- Content Planning, Organization, and Distribution:
- Content Calendar Tools: Such as Schedule, Trello, or Google Calendar.
- Content Management Systems (CMS): Like WordPress, Drupal, or Joomla for publishing and managing content.
- Keyword Research and SEO:
- Google Keyword Planner: In order to search relevant keywords.
- SEMrush or Ahrefs: For in-depth SEO analysis.
- Yoast SEO (WordPress plugin): To optimize on-page SEO.
- Social Media Management:
- Hootsuite, Buffer, or Sprout Social: For scheduling and managing social media posts.
- Social media analytics tools: To track performance on different platforms.
- Email Marketing and Outreach:
- Mailchimp, Constant Contact, or HubSpot: For email marketing campaigns.
- Mailshake: For personalized outreach and email campaigns.
- Content Promotion and Analytics:
- Buffer or Hootsuite: To schedule and automate content sharing.
- Outbrain or Taboola: For native advertising and content promotion.
- BuzzSumo: To find influential content and influencers in your niche.
- Analytics and Performance Tracking: Including Google Analytics, Google Search Console, and social media analytics tools.
- Visual Content Tools:
- Adobe Spark: For crafting web narratives and visual content for social media.
- Animoto: To make videos easily with templates.
- Piktochart: For creating infographics.
- Project and Team Collaboration:
- Asana, Trello, or Basecamp: To manage content projects and collaborate with team members.
- Slack: For team communication and collaboration.
- Content Curation and Research:
- Feedly or Flipboard: For finding and curating relevant industry content.
- Pocket: To save articles and content for later reference.
- BuzzSumo: To discover trending and popular content in your niche.
- Google Alerts: For tracking mentions of specific keywords or topics.
- Content A/B Testing:
- Optimizely or VWO (Visual Website Optimizer): For testing different versions of content or landing pages.
- Lead Generation and Forms:
- Leadpages or Unbounce: For creating landing pages and lead generation forms.
Conclusion:
Content marketing, as defined by Joe Pulizzi and championed by Seth Godin, stands as a pivotal force in modern marketing. It emphasizes the deliberate creation and distribution of valuable content to build trust and lasting connections with a defined audience.
This multifaceted approach offers businesses a versatile toolkit to inform, engage, and educate. However, it’s not without its challenges; it demands time, consistency, and creativity.
In essence, content marketing is an investment in the future of businesses, nurturing trust, engagement, and authority in the digital landscape.
